In the United States, a man simply took a hot shower and literally almost froze to death when he got out. The person actually developed a serious allergic reaction to low temperatures. What caused it?
Some clinical cases are very surprising and sometimes turn out to be unusual. In 2019, for example, a man was affected by a complete calcification in the penis. It was a very serious form of Peyronie's disease. In a publication in The Journal of Emergency Medicine on October 27, 2020, doctors from the School of Medicine at the University of Colorado (United States) describe the case of a man who almost lost his life after being got out of his shower. The 34-year-old just took a hot shower before leaving. The family found him lying on the ground with difficulty breathing and patches of hives on his skin. According to doctors, the man developed a very serious allergic reaction to low temperatures.
The authors of the publication mention anaphylaxis, a dangerous allergic reaction. When help arrived, the patient nevertheless explained that he had already had allergic reactions to cold temperatures with the appearance of hives. The person claimed that his first allergic reactions to the cold started after his return from Micronesia (Oceania), where the climate is tropical.
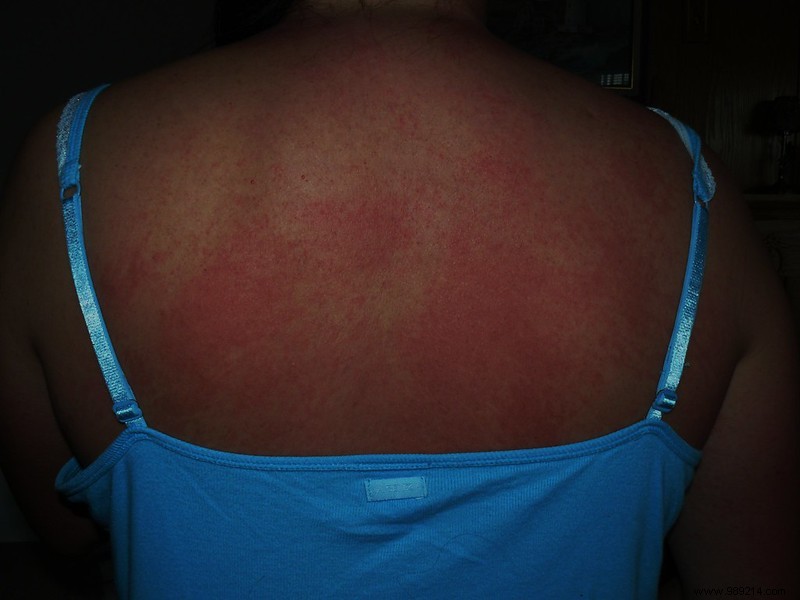
Doctors treated the patient with epinephrine and oxygen before he arrived in the emergency room. In the hospital, he was sweating profusely and covered in patches of hives. Thus, the doctors diagnosed him with cold urticaria. It is an allergic reaction of the skin when it is exposed to cold, whether it is air or water. The appearance of an itchy rash is the most common symptom. However, more serious cases can generate an anaphylactic reaction. This can cause a drop in blood pressure and narrowing of the airways.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctors performed a ice cube test . It was simply a matter of placing an ice cube on the patient's skin for five minutes. If a bump appears, the diagnosis of hives is confirmed. The cause of this phenomenon remains unknown. It may be a genetic predisposition which can be transmitted from generation to generation or even as a reaction following a viral infection, or even certain cancers.