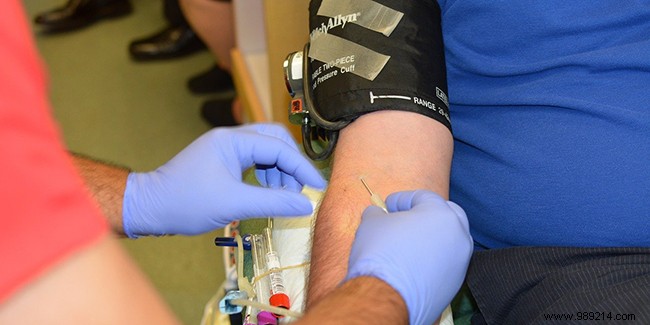
Anyone between the ages of 18 and 70 who is in good health and weighs more than 50 kg can donate blood. However, there are contraindications in some cases and, from the age of 50, it is no longer possible to make all types of blood donation.
There are 3 different types of blood donation. Depending on the age of the donor in particular, some are authorized, others are not.
The most common donation is called “whole blood donation”. The blood collected is used for blood transfusions, but also for medical research.
Then it is possible to donate plasma, i.e. the liquid part of blood also known as serum. This type of donation is used, for example, in the preparation of vaccines, treatments for hemophilia (an inherited disease that prevents the blood from clotting), or even to prevent rhesus-related neonatal disease (when the rhesus of the mother is different from the unborn baby).
Finally, blood donation can also take the form of blood platelet donation, cells that play a role in blood clotting. This donation is used to treat certain cancers, and in particular leukemia.
Anyone over the age of 70 can donate blood if they are in good health and weigh more than 50 kg.
The number of blood donations is nevertheless limited according to its nature and the gender of the donor for some of them. A woman can donate whole blood a maximum of 4 times a year, 6 times for men. An interval of 8 weeks between 2 of this type of blood donation is required. A man and a woman can donate plasma 24 times in a year, with a 2-week delay between these donations. Finally, with regard to blood platelet donations, the maximum number per year is 12 times for both sexes, with a minimum interval of 4 weeks between two donations.
On the other hand, certain circumstances impose a deadline to be able to donate blood:2 weeks after the end of the symptoms of a viral disease; 7 days to 4 months after surgery; 4 months after a tattoo or piercing; 6 months after giving birth; and variable delays for those returning from an area at risk for malaria.
Some people cannot give blood at all. These are those who have undergone a transfusion and/or a transplant, who are likely to transmit through blood, a bacterium, a virus or a parasite leading to diseases or a viral infection through sexual contact, women pregnant and people who have lived in the United Kingdom for at least 1 year between 1980 and 1996.
In all cases, before any blood donation, a medical examination is performed and the donor must answer a questionnaire to judge his state of health and whether or not he can donate blood.
The French Blood Establishment (EFS) also provides an interactive questionnaire on its website that allows you to find out whether or not a person is eligible to donate blood.
Although blood donation is authorized for all healthy people between the ages of 18 and 70, certain restrictions concerning in particular the nature of the donation are applied.
Thus, from the age of 50, the donation of granulocyte (white blood cells, a type of leukocyte) is no longer authorized. People aged 65 and over can only donate whole blood on the condition that a doctor gives authorization.
From the age of 70, it is no longer possible to donate blood, except in exceptional cases, for example if the senior has rare type blood.
Also note:people aged 60 and over who donate blood for the first time must be authorized to do so by the doctor in charge of the establishment taking the blood sample.